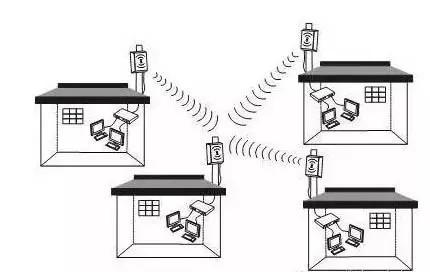
The commonly used wireless short-range communication languages ​​and technologies in the Internet of Things include: Huawei Hilink protocol, WiFi (IEEE 802.11 protocol), Mesh, Bluetooth, ZigBee, Thread, Z-Wave, NFC, UWB, and LiFi.
Language is the most important human communication tool and it is the main expression of communication and communication. In the era of the Internet of Things, when machines need to communicate, they also need to understand each other in a language that they can understand. Today, we will take a look at those wireless short-distance communication languages ​​and technologies commonly used in the Internet of Things--Huawei Hilink Protocol, WiFi (IEEE 802.11 Protocol), Mesh, Bluetooth, ZigBee, Thread, Z-Wave, NFC, UWB, LiFi.
1. Huawei Hilink Protocol
In December last year, Huawei launched a self-developed "three-piece" smart home - Hilink protocol, Huawei-LiteOS system and IOT chip. At present, various Internet end-users' interconnection and interoperability agreements on the market are already being put into competition, but they do not seem to be friendly to each other and are isolated from each other. They are behind closed doors. The Hilink protocol is known as “Putonghua†among smart devices. It can automatically discover devices and connect them at the touch of a button. It is also compatible with protocols such as ZigBee, WiFi, and Bluetooth.
2. WiFi/IEEE 802.11 protocol
WiFi, full name Wireless-Fidelity, wireless fidelity, is a standard in wireless local area networks (WLAN). Since its launch in 1999, it has been one of the more commonly used ways of accessing the Internet in our lives. WiFi technology usually uses 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz surrounding frequency bands. By connecting a wireless router through a wired network, the wired signal can be converted into a WiFi signal. The WiFi standard family also has 802.11a, 802.11b, 802.11g, and 802.11n.
The WiFi 802.11ah WiFi standard announced in 2016 by the WiFi Alliance has enabled WiFi to be used in more places such as: Small-sized, battery-powered wearable devices are also suitable for deployment in industrial facilities, and in both cases. The application between. HaLow uses the 900MHz band, which is lower than the current WiFi 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands. Lower power consumption, while HaLow's coverage can reach 1 km, the signal is stronger, and it is not easily disturbed. These features make WiFi more responsive to the development of the Internet of Things.
Advantages: Wide coverage, fast data transfer rate.
Disadvantages: poor transmission security, poor stability, slightly higher power consumption, and poor networking.
3. Mesh/IEEE 802.11s protocol
The wireless mesh network, known as the cheap "Last Mile" broadband access scheme, utilizes a multi-hop wireless mesh architecture to provide broadband access for mobile users. Mesh is a combination of WLAN and mobile Ad Hoc (peer-to-peer) networks. Compared with the WLAN, each network terminal can perform direct communication between peers, and no longer needs to be forwarded by the AP (base station), and the coverage is larger. Compared with Ad Hoc, due to the fixed and power-supply backbone routers, there is no need to consider too much in terms of mobility and power consumption.
Advantages: Fast network deployment, no complicated configuration; stable network, any node is broken, does not affect data transmission from other devices; network coverage is wide, and can be connected with multiple broadband wireless access technologies (such as WLAN, WiMAX, UWB, 3G, etc.) The combination of them forms a larger multi-hop network structure.
Disadvantages: With a certain degree of delay, it is not suitable for real-time monitoring applications, and the network capacity is limited.
4. Bluetooth/IEEE 802.15.1 protocol
The Bluetooth technology first began in 1994 and was developed by Sweden Ericsson. It uses frequency-hopping spread spectrum and the communication frequency band is 2.402G Hz-2.480GHz. Up to now, 9 versions have been updated, namely Bluetooth 1.0/1.1/1.2/2.0/2.1/3.0/4.0/4.1/4.2, and the communication radius extends from a few meters to several hundred meters.
Bluetooth technology is widely used in mobile phones, PDAs and other mobile devices, PCs, GPS devices, and a large number of wireless peripheral devices (Bluetooth headsets, Bluetooth keyboards, etc.).
Bluetooth technology also follows the development of the Internet of Things. The latest Bluetooth 4.2 data transfer rate up to 1Mbps, more powerful privacy features, Ipv6 network support. In the field of smart homes, Bluetooth devices using the Bultooth Smart technology may not be able to communicate between devices and devices. This can solve the case of sudden disconnection without WiFi, smart home equipment will still be able to continue to work.
Advantages: Fast speed, low power consumption, high security.
Disadvantages: There are few network nodes and it is not suitable for multi-point deployment.
5. ZigBee/802.15.4 agreement
Zigbee was formally proposed in 2003. It appeared to compensate for the high complexity of the Bluetooth communication protocol, large power consumption, proximity, and small size of the network. The name is taken from the bee, and the bee (bee) flies through the "dance" of fluttering and "zigs" to communicate the position information of the pollen with the companion, and this way constitutes a communication network in the group.
ZigBee can operate in three frequency bands: 868MHz-868.6MHz, 902MHz-928MHz, and 2.4GHz-2.4835GHz. The last frequency band is universal in the world, with 16 channels, and this band is a toll free, application-free radio frequency band. The three band transmission rates are 20 kbps, 40 kbps, and 250 kbps, respectively.
ZigBee uses the ad hoc network to communicate and is the most famous wireless communication protocol in the field of wireless sensor networks. In a wireless sensor network, when a certain sensor's message cannot be delivered smoothly from a certain communication path, the dynamic router will quickly find another close-up channel transmission data, thus ensuring the reliable transmission of information.
ZigBee is not a mainstream wireless communication technology, but it is highly sought after by some manufacturers for its low power consumption, low cost, low speed, high capacity, and long battery life. For example, Xiaomi launched a series of home smart products in 2015, all support ZigBee communication, and the recent launch of millet temperature humidity sensor.
Advantages: high security, low power consumption, strong networking capacity, large capacity, long battery life.
Disadvantages: high cost, poor anti-interference, ZigBee protocol is not open source, communication distance is short.
6.Thread /IEEE 802.15.4 agreement
Both Thread and ZigBee belong to 802.15.4, but great improvements have been made to 802.15.4. Thread is a protocol built on top of IPv6. It does a great job of optimizing transmission security and system reliability. It can carry the AllSeen of Qualcomm Haier's dozens of enterprise groups and the Internet of Things, and it can also support Apple's Homekit smart home platform. Thread was designated as the only communication protocol of the household IoT, and Nest initiated industry alliances. The alliance members jointly promoted the Thread protocol. Thread short-range communication is also promising.
7. Z-Wave protocol
The Z-Wave wireless networking specification was introduced in 2004, led by Danish chip and software developer Zensys, and the Z-wave Alliance promotes its application. Z-Wave operates at 908.42MHz in the United States and 868.42MHz in Europe and uses wireless mesh network technology. Therefore, any node can directly or indirectly communicate with other neighboring nodes in the communication range. Data rates include 9.6kbps and 40kbps. Output power is 1mW and 0 dBm. The effective coverage of the signal is 30m indoors and over 100m outdoors. Z-Wave is an emerging radio frequency-based, low-cost, low-power, high-reliability, short-range, narrow-bandwidth application.
Z-Wave focuses on home automation. It is more popular in European and American countries. It enters the Chinese market later than Zigbee, and its market share is far behind Zigbee. Because of the frequency band division, although it can develop in China, it is also cautious.
Advantages: Simple structure, low speed, low power consumption, low cost, long transmission distance relative to ZigBee, high reliability.
Disadvantages: The standard is not open, the chip can only be obtained through the sole source of Sigma Designs.
8.NFC
NFC, near field communication, was jointly developed by Philips Semiconductors, Nokia, and Sony in 2002. In 2004, the NFC Forum was established to focus on the standardization and promotion of near field communication technology. The technology evolved from the integration of RFID and interconnection technology. NFC is a short-range high-frequency radio technology with an operating frequency of 13.56 MHz and a distance of 20 cm. Its transmission speed is 106 Kb/s, 212 Kb/s or 424 Kb/s. Through the card, card reader and point-to-point three business models for data reading and exchange.
NFC and Bluetooth technology are similar in function, but the transmission speed and transmission distance are not as fast and far away from Bluetooth. At the same time, the power consumption and cost are low, and the confidentiality is good. These advantages make it the darling of mobile payment and consumer electronics.
Recently, the apple pay and the Samsung pay have become very popular in the field of mobile payment. The importance of NFC technology in the future of the mobile IoT world is self-evident.
9.UWB
UWB, UWB, a carrierless communication technology, uses nanosecond to picosecond non-sinusoidal narrow pulses to transmit data, enabling data transfer rates of hundreds of Mb/s to several Gb/s in a range of approximately 10m . UWB has many advantages such as strong anti-interference performance, high transmission rate, wide bandwidth, low power consumption, and low transmission power. It is mainly used in indoor communication, high-speed wireless LAN, home network, cordless telephone, security detection, location measurement, radar, etc. field.
What is more interesting is that the standardization of UWB has always been controversial, which also indirectly slows down the pace of its promotion. Compared with wireless communications such as Bluetooth, 802.11b, and 802.15, UWB can provide faster, more distant and wider transmission rates, and more and more researchers are investing in UWB.
10.LiFi
LiFi, optical fidelity technology, is a new wireless transmission technology that uses visible light spectrum (such as light emitted from a light bulb) for data transmission. It was invented by Prof. Harald Hass, University of Edinburgh, UK. LiFi is equivalent to Wi-Fi's visible light wireless communication (VLC) technology, which utilizes light wave transmission data from light emitting diode (LED) bulbs to provide lighting and wireless networking at the same time, without electromagnetic interference, which can help alleviate current network traffic bursts. Increased questions.
All kinds of transmission technologies have their own strengths and shortcomings, and they hope to see them shine in the world of the Internet of Things. We also expect more companies like Huawei to use “Putonghua†in the industry to help the Internet of Things industry and bring us to a more comfortable and comfortable modern life.
Hitachi Elevator Spare Parts, Hitachi Elevator Parts
Hitachi has been developing and manufacturing elevators and escalators for about 90 years. Social demands on elevators and escalators changed dramatically over time: faster, larger, and barrier-free and required.
History of Hitachi's Elevator and Escalator Business
-
1924Lift manufacturing at the Kameido plant
-
1932First elevator delivered (to Tokyo Electric Power)
-
1937First escalator delivered (to Osaka Railway Department Store)
-
1956Hitachi Building Services Co., Ltd. founded (currently known as Hitachi Building Systems Co., Ltd.)
-
1966Hitachi Elevator Engineering Co .,( 1514313,Hong Kong) Ltd. founded in Hong Kong
-
1967Construction of an elevator research tower in the Mito plant completed (90m in height)
-
1968300m â„ minute ultra high speed elevator delivered to the Kasumigaseki Building, Japan's first skyscraper
-
1972Hitachi Elevator Engineering (Singapore) Pte. Ltd. founded in Singapore
-
1974Delivery of 540m â„ minute elevators to skyscrapers in Shinjuku
-
1987Hitachi Mito Engineering Co., Ltd. founded
-
1991Siam-Hitachi Elevator Co., Ltd. Founded in Thailand
-
1998Three affiliated companies in China merged to found Guangzhou Hitachi Elevator Co., Ltd.
-
2003Opened Hitachi Building Solution Lab
-
2007Guangzhou Hitachi Elevator Co., Ltd. renamed to Hitachi Elevator (China) Co., Ltd.
-
2008Hitachi Lift India Pvt. Ltd. foundedDelivered the world's highest class ultra fast double deck elevators to the Shanghai World Financial Center
-
2009Introduction of the Company systems leads to the establishment of the Urban Planning and Development Systems Company
-
2010Completed elevator research tower [G1TOWER" (213m in height) for Mito WorksFounded Hitachi Elevator Asia Pte. Ltd. as a general elevators and escalators business company for the Southeast Asia, India, and Middle East regionsCompleted elevator research tower (172m in height) for Hitachi Elevator (Shanghai) Co. Ltd.
-
2011Founded Hitachi Elevator Philippines CorporationDelivered 600m â„ minute elevators to the Al Hamra Mixed-Use Complex in Kuwait.