An EV battery typically consists of thousands of rechargeable lithium-ion cells connected together to form the battery pack. Lithium-ion cells are widely used due to their cost efficiency and ability to provide the best balance between energy storage capacity and price.
The Rise of Electric Mobility and EV Battery Production
With the continuous growth of electric mobility, the demand for electric vehicles (EVs) and their batteries is rapidly increasing. This raises the question: how can battery manufacturers meet this growing demand, and what materials are required to produce an EV battery? In this article, we will delve into the materials used for EV batteries and the manufacturing processes involved. We'll also explore the leading EV battery manufacturers and what the growing supply and demand gap means for the future of EV batteries.
What Are EV Batteries Made Of?
EV batteries come in a variety of shapes and sizes, from the type of cells to their chemical composition. Before we dive into the materials used in EV batteries, it’s important to understand the different physical cell structures. 
Types of EV Battery Cells
Three basic types of battery cells are commonly used in electric vehicles: cylindrical cells, prismatic cells, and pouch cells. Although coin cells exist, they are currently only used for research and development purposes and are not yet commercialized for EVs.
1. Cylindrical Cells
Cylindrical cells are perhaps the most widely used format. As the name suggests, they are contained within a cylindrical casing that provides resistance against mechanical shocks—similar to standard AA or AAA alkaline batteries. Due to their widespread use, cylindrical cells are the most cost-effective and easy to manufacture. However, they may have limitations in terms of power output, which is why EVs with smaller batteries often opt for prismatic or pouch cells.
2. Prismatic Cells
Unlike cylindrical cells, which are relatively small, prismatic cells can be up to 20 to 100 times larger. They use less material for the casing, allowing them to store more energy and deliver higher power while managing heat more effectively than cylindrical cells. Although less common than cylindrical cells, their use is growing, and they may soon dominate a significant portion of the market.
3. Pouch Cells
As their name suggests, pouch cells are encased in a flexible plastic casing, making them highly efficient in terms of space usage. However, their delicate casing requires additional protection to prevent mechanical damage.
Popular Materials Used in EV Batteries
Beyond their format, EV battery cells also differ based on their chemistry—the materials used to store electricity. Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries are the most widely used due to their relatively low cost and high energy storage capacity. Other popular battery chemistries include Nickel Manganese Cobalt (NMC) and Nickel Metal Hydride (Ni-MH), which were initially favored for their affordability, longevity, and high capacity. Older hybrid models, such as the Toyota Prius and RAV4, often used NMC or Ni-MH batteries.
Lead-acid cells are among the oldest types of batteries used in vehicles. Decades before they were used in EVs, lead-acid batteries were—and still are—used in gas-powered vehicles to power their ignition. Unlike most other EV battery types, lead-acid cells can be easily repaired and maintained by car mechanics and require minimal upkeep. However, they cannot store as much energy as other battery types, making them unsuitable for larger EVs.
What Are Lithium-Ion Batteries Made Of?
It’s no surprise that lithium-ion batteries contain lithium. But have you ever wondered what other materials are needed to make a Li-ion battery?
Creating a lithium-ion battery requires multiple components. Like other batteries, Li-ion batteries have a positively charged cathode, a negatively charged anode, and an electrolyte that separates them. The cathode is typically made from a mix of lithium, nickel, cobalt, and manganese, while the anode is most commonly made using graphite. Finally, the individual cells are enclosed in an aluminum or steel casing that holds the battery pack together and protects it against mechanical damage. 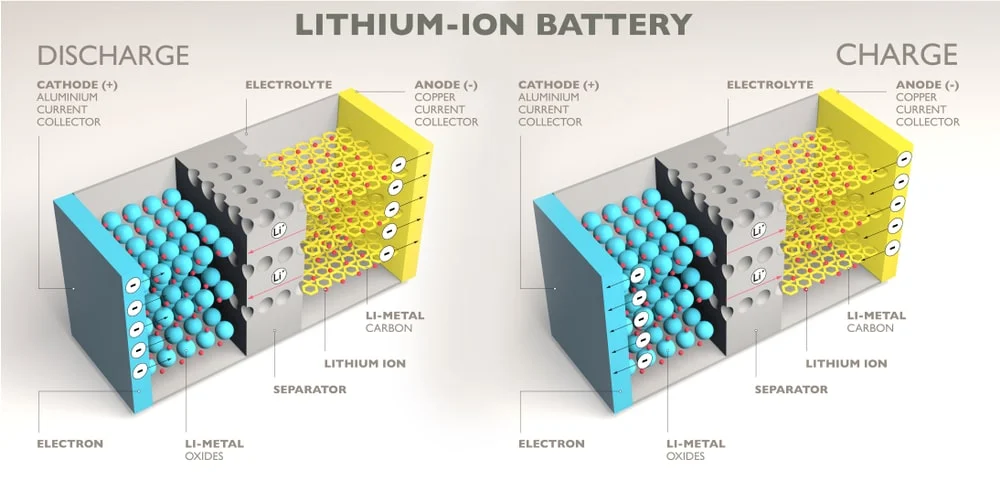
Key Components Needed for the Battery
Beyond the raw materials that make up its cells, an EV battery requires numerous hardware and software components to function properly. Let’s take a closer look at the main features of an EV battery.
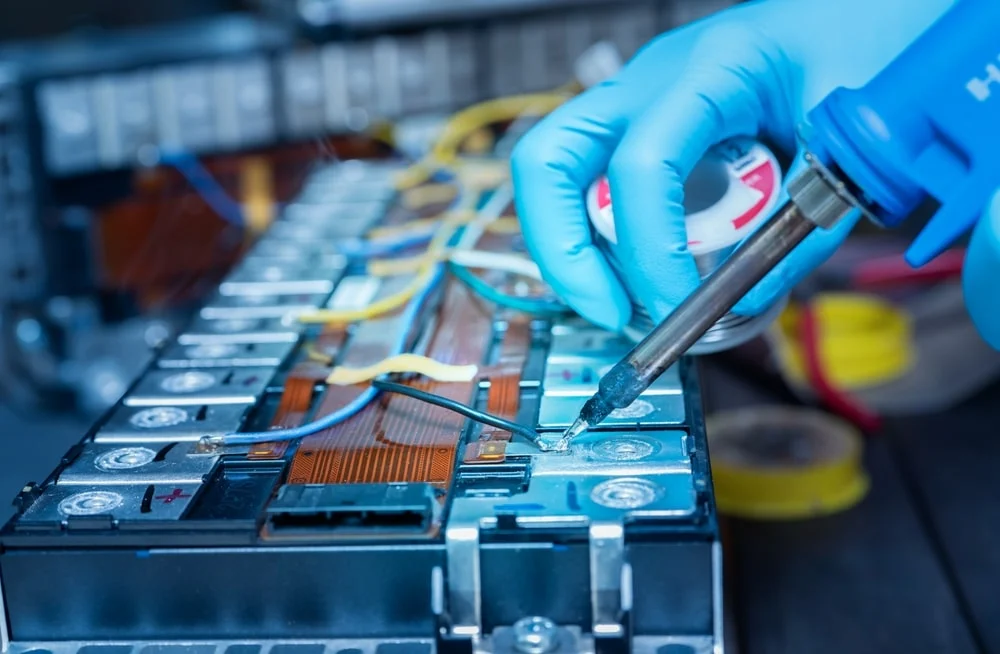
Battery Module Array
The battery module array refers to the power-storing components of the battery. This includes the individual cells, which are grouped into modules containing a specific number of cells wired together. These modules are then connected to form the final, full-sized battery pack, what most people commonly refer to as the EV battery.
Battery Management System
An EV’s battery management system (BMS) is perhaps the most crucial part of its battery. The BMS controls every aspect of the battery and ensures optimal performance. For example, it monitors and regulates each cell’s charge level, decides which cells to charge or discharge, and tracks the battery pack’s temperature. If any aspect of the battery’s operation deviates from normal values, the BMS can automatically adjust energy usage to protect the battery pack and, if necessary, alert the driver.
Battery Electrical System
The battery electrical system encompasses all the wiring, connections, fuses, and other electrical components needed to operate an EV battery. It is designed to handle high voltages and is typically integrated with the battery management system to efficiently manage each cell.
Battery Cooling System
Just like your phone or laptop’s battery heats up with use, so do EV batteries. Given their size, electric car batteries can generate a lot of heat that needs to be dissipated—this is the responsibility of the battery cooling system. Typically, this involves a sealed coolant that carries heat away from the battery cells and dissipates it in the air.
Battery Protection Case
Lastly, the battery needs a physical structure to hold all its components together. This is the role of the battery protection case. While its function may seem straightforward, its design must ensure it is airtight, waterproof, flame-retardant, and resistant to various shocks and vibrations, making its engineering far more complex than it appears.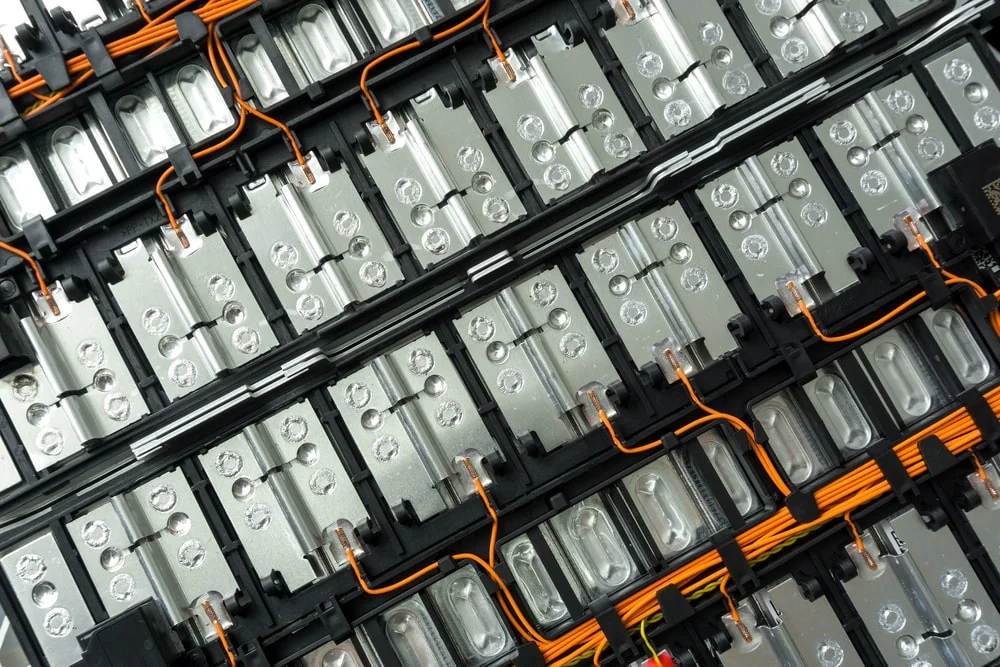 
Who Manufactures Them?
Given the resource-intensive nature of EV battery production, most of the world’s battery production is controlled by a few major companies. The leading EV battery manufacturer globally is CATL (Contemporary Amperex Technology Co. Limited), a Chinese company with approximately 34% of the total EV battery market share. This is unsurprising since China holds 70% of the production capacity for cathodes and 85% for anodes, and more than half of the raw materials used to make an EV battery also come from China.
The second-largest manufacturer is LG Energy Solution, which holds 14% of the market share. Recently, they announced a partnership with Honda to invest $4.4 billion in building an EV battery manufacturing plant in the U.S., expected to begin production around 2025.
The third-largest manufacturer is BYD, a Chinese company with a 12% market share. Unlike many of its competitors, BYD is also an EV manufacturer, meaning it can meet the majority of its own battery and EV system needs.
The U.S., Japan, and South Korea account for the remaining portions of the EV battery market, respectively holding 7%, 11%, and 14% of global EV battery production. Clearly, China dominates the EV battery manufacturing landscape. While the U.S. and EU are attempting to develop domestic production through public sector initiatives, China is likely to remain the leading supplier of EV batteries until at least 2030.
Supply and Demand Gap
Driven by the rapid expansion of electric mobility, EV manufacturers face challenges in sourcing the necessary raw materials for making EVs, particularly batteries. Since the beginning of 2020, the automotive sector has been grappling with ongoing shortages of computer chips, which continue to impact EV production costs. Adding to existing lithium shortages, another looming shortage of minerals, specifically graphite, threatens further disruptions.
Graphite is the primary component of an EV battery’s anode, and shortages could drive up the price of producing EV batteries even more.
The Future of EV Batteries
With news of shortages and rising prices everywhere, you might wonder what the future of EV batteries looks like. Beyond mining for more raw materials, one promising avenue is EV battery recycling, which recovers many of the minerals from old batteries and reuses them for new battery production. Not only can this alleviate current shortages, but it also makes EV battery production much more sustainable.
In addition to recycling, new research aims to enhance EV battery performance, making them more efficient and reducing the need for raw materials.
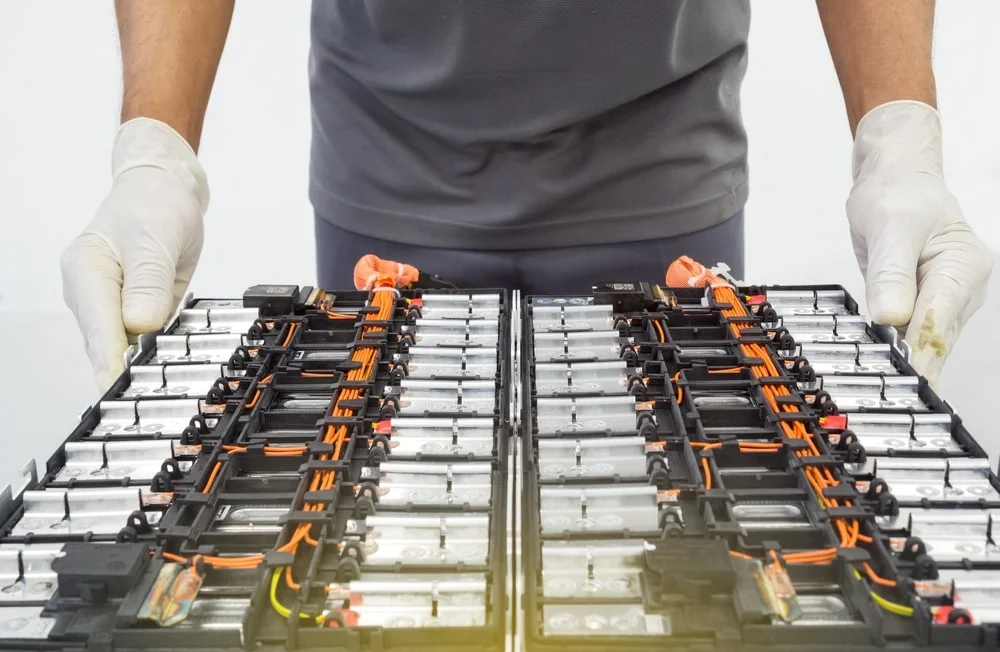

EV battery manufacturing is a complex process that relies on materials in increasingly short supply and expertise that few manufacturers possess. However, advancements in battery recycling and research into more efficient batteries, combined with policy efforts to boost global production, should ensure EV batteries remain affordable and accessible for years to come.
If you're interested in learning more about EV batteries, check out our dedicated articles on their cost or recycling possibilities.
Â
Capsule Filling Machine Accessory Equipment
Capsule Sorting Polisher,Capsule Polishing Machine,Capsule Filling Machine Accessory Equipment,Vertical Capsule Sorting Polisher
ZHEJIANG FUCHANG MACHINERY CO., LTD. , https://www.fuchangmachinery.com