Introduction to 300 Series Austenitic Stainless Steel
In the world of materials science, stainless steel has become a cornerstone of modern engineering. Among its many types, the 300 series austenitic stainless steels stand out for their remarkable combination of strength, flexibility, and corrosion resistance. These alloys are widely used in industries ranging from food processing to medical devices due to their durability and adaptability. The most well-known grades in this family are 304 and 316, both of which are often considered top-tier options for their performance and versatility.
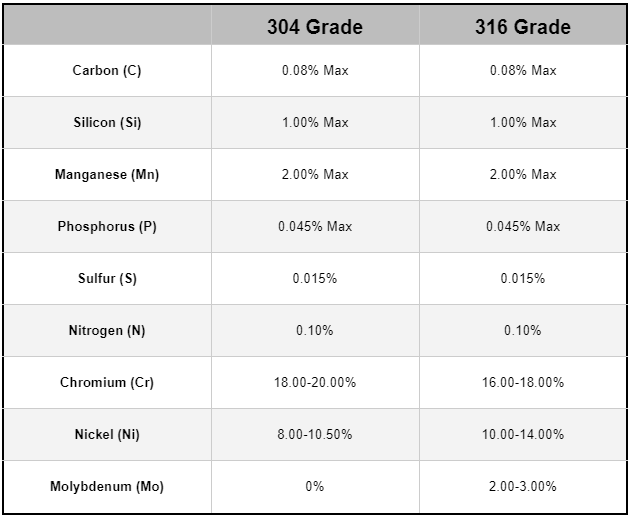
The Foundation of Stainless Steel: Chromium
At the core of all stainless steels is chromium, an element that plays a crucial role in preventing rust and degradation. When exposed to air, chromium reacts with oxygen to form a thin, protective oxide layer on the surface of the metal. This passive film not only prevents further oxidation but also gives the material its characteristic "stainless" appearance. To qualify as stainless steel, the alloy must contain at least 10.5% chromium, though higher percentages can significantly enhance its resistance to corrosion and wear.
304 Stainless Steel: The Versatile Workhorse
Among the 300 series, 304 stainless steel is one of the most commonly used grades. Known for its balanced composition of 18% chromium and 8% nickel, it offers excellent corrosion resistance, good formability, and ease of fabrication. Its widespread use spans across kitchens, hospitals, and construction sites, where it’s valued for its reliability and cost-effectiveness. While it performs well in general environments, it may not be the best choice for highly corrosive or saline conditions.
316 Stainless Steel: The Corrosion-Resistant Champion
When it comes to resisting harsher environments, 316 stainless steel takes the lead. This grade includes molybdenum (typically around 2%) in addition to its 16% chromium and 10% nickel content. Molybdenum enhances the steel's ability to resist pitting and crevice corrosion, especially in marine or chloride-rich settings. As a result, 316 is often the preferred choice for chemical processing, offshore structures, and medical equipment where long-term durability is essential.
A Comparative Look: 304 vs 316 Stainless Steel
While both 304 and 316 are part of the 300 series and share many similarities, they serve different purposes. 304 is ideal for everyday use in less aggressive environments, while 316 excels in more demanding conditions. For example, in coastal areas or industrial zones with high salt exposure, 316 provides better protection against corrosion. Choosing between them depends on the specific application and environmental factors involved.
Welding and Forming: The Common Strengths
One of the major advantages of 300 series stainless steels is their excellent weldability and formability. They can be easily shaped into complex designs without losing structural integrity. However, unlike some other metals, these alloys cannot be hardened through heat treatment. Instead, they gain strength through cold working processes. For applications requiring high-quality welds, low-carbon variants like 304L and 316L are often recommended, as they reduce the risk of intergranular corrosion during welding.
Typical Uses Across Diverse Industries
The versatility of 304 and 316 stainless steels makes them suitable for a wide range of industries. 304 is commonly found in kitchen appliances, countertops, and architectural elements, where aesthetics and durability matter. On the other hand, 316 is frequently used in marine equipment, chemical tanks, and medical devices, where exposure to harsh chemicals or saltwater is common. Although 316 is more expensive, its enhanced performance justifies the cost in critical applications.
Beyond the standard grades, there are also super austenitic stainless steels, which offer even greater resistance to corrosion and extreme temperatures. These advanced materials are used in specialized fields such as aerospace, oil and gas, and high-performance manufacturing, where traditional grades might fall short.
Compositions of Austenitic Stainless Steel
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What makes 304 and 316 stainless steel resistant to corrosion?
Both grades owe their corrosion resistance to high chromium content, which forms a protective oxide layer. Additionally, 316 contains molybdenum, which further improves its resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion, especially in chloride-rich environments.
2. How does the addition of molybdenum enhance the properties of 316 stainless steel?
Molybdenum increases the steel’s ability to resist localized corrosion, particularly in seawater and acidic conditions. This makes 316 more durable in environments where 304 might degrade over time.
3. What are super austenitic grades, and how do they differ from 304 and 316?
Super austenitic stainless steels are advanced versions of the 300 series, containing higher levels of nickel and molybdenum. They offer superior resistance to corrosion, oxidation, and mechanical stress, making them ideal for extreme conditions such as deep-sea exploration or chemical processing plants.
Shop Stainless Steel Instrumentation Fittings
Shop Stainless Steel Cast 150# Fittings
Shop Stainless Steel Nipples
Shop Stainless Steel Forged 3000# Fittings
Shop Stainless Steel Flanges
Shop Stainless Steel Weld Fittings
Shop Stainless Steel Tubing
.Perilla Seed
1. Lower lipids and blood pressure
The rich linolenic acid in Perilla Seed Oil can reduce serum cholesterol, triglycerides, low-density lipoprotein and very low-density lipoprotein, thereby inhibiting thrombosis and preventing myocardial infarction and cerebral infarction. In addition, α-linolenic acid Acid can also reduce blood viscosity, increase blood oxygen-carrying capacity, inhibit the synthesis of triglycerides, and increase the metabolism of various lipids in the body. Therefore, perilla seed oil has a particularly obvious effect in lowering lipids and blood pressure, especially for hyperlipidemia. and borderline hypertension, the effect is more prominent.
2. Protect liver
The α-linolenic acid in perilla seed oil can effectively inhibit fat synthesis, break down fat and excrete it from the body. Daily consumption can prevent the formation of fatty liver.
3. Strengthen the brain and protect eyesight
CCTV's "Encyclopedia Quest" reported that α-linolenic acid is one of the basic raw materials for nerve cell synthesis and a key nutrient that determines the development of human intelligence. It is called "brain gold". Correct supplementation of linolenic acid can improve the IQ and intelligence of infants and young children. Increase by 20%-30%, pregnant women and children must supplement.
Perilla Frutescens Seed,Perilla Seed Oil Omega 3,Perilla Seed Eating,perilla Seed Benefits
Jilin Chunyi Industrial Co., Ltd , https://www.perillaseed.com