Introduction to 300 Series Austenitic Stainless Steel
In the world of materials science, stainless steel has become a cornerstone of modern engineering. Among its many types, the 300 series austenitic stainless steels stand out for their remarkable combination of strength, flexibility, and resistance to rust and corrosion. These grades, especially 304 and 316, are widely used in industries ranging from healthcare to construction due to their high-quality performance and adaptability.
The Foundation of Stainless Steel: Chromium
Chromium is the key ingredient that makes stainless steel "stainless." It forms a thin, protective oxide layer on the surface when exposed to oxygen, which prevents rust and corrosion. This self-healing layer is what gives all stainless steels their characteristic durability, making them ideal for use in harsh environments.
304 Stainless Steel: The Versatile Workhorse
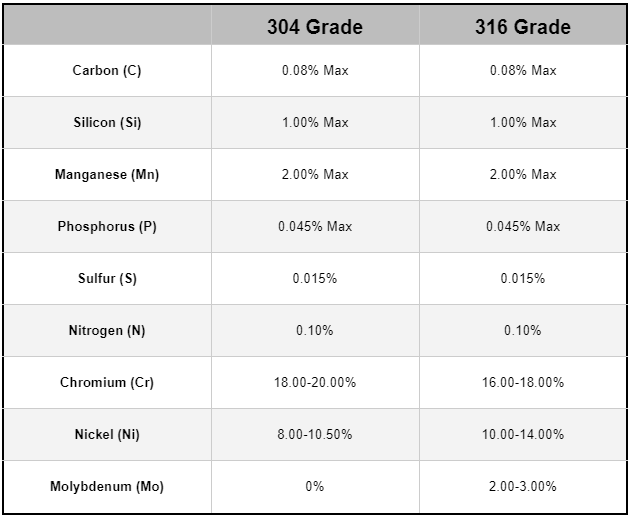
304 stainless steel is one of the most commonly used alloys in the 300 series. With an average composition of 18% chromium and 8% nickel, it offers excellent corrosion resistance and good mechanical properties. Its versatility allows it to be used in everything from kitchenware and food processing equipment to architectural structures and industrial components.
316 Stainless Steel: The Corrosion-Resistant Champion
316 stainless steel takes corrosion resistance a step further by adding molybdenum to its composition. This element enhances its ability to resist pitting and crevice corrosion, especially in chloride-rich or marine environments. As a result, 316 is often preferred in chemical plants, marine applications, and medical devices where long-term durability is essential.
A Comparative Look: 304 vs 316 Stainless Steel
While both 304 and 316 are popular choices, they serve different purposes. 304 is more cost-effective and suitable for general-purpose use, while 316 is ideal for environments with high exposure to chlorides or chemicals. Choosing between them depends on the specific demands of the application and the level of corrosion resistance required.
Welding and Forming: The Common Strengths
Austenitic stainless steels like 304 and 316 are known for their excellent formability and weldability. They can be easily shaped into complex designs without losing structural integrity. However, unlike some other stainless steels, they cannot be hardened through heat treatment. Instead, their strength can be increased through cold working processes. For welding-heavy applications, the low-carbon variants (such as 304L and 316L) are often recommended to reduce the risk of intergranular corrosion.
Typical Uses Across Diverse Industries
304 stainless steel is widely used in kitchens, commercial buildings, and public infrastructure due to its balance of aesthetics and functionality. On the other hand, 316 is favored in environments where exposure to saltwater, acids, or aggressive chemicals is common, such as in offshore platforms, pharmaceutical equipment, and medical instruments.
Both grades also find use in the manufacturing of pipes, valves, and fittings, especially in industries where hygiene and durability are critical factors.
Super Austenitic Grades: Extending Performance
Beyond the standard 304 and 316 grades, there are super austenitic stainless steels that offer even greater resistance to corrosion and oxidation. These high-nickel alloys are designed for extreme conditions, such as high-temperature environments or highly corrosive chemical settings, where regular austenitic grades may not perform as well.
Compositions of Austenitic Stainless Steel
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What makes 304 and 316 stainless steel resistant to corrosion?
The primary factor is the presence of chromium, which creates a passive oxide layer on the surface. In the case of 316, the addition of molybdenum enhances its ability to resist corrosion in harsher environments, particularly those with chlorides.
2. How does the addition of molybdenum enhance the properties of 316 stainless steel?
Molybdenum improves the alloy's resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion, especially in saline or chloride-rich conditions. This makes 316 a preferred choice in marine and chemical applications where corrosion is a major concern.
3. What are super austenitic grades, and how do they differ from 304 and 316?
Super austenitic grades contain higher levels of nickel and other elements, providing enhanced resistance to corrosion and oxidation. They are typically used in more extreme conditions than standard 304 or 316 grades, offering superior performance in demanding environments.
Shop Stainless Steel Instrumentation Fittings
Shop Stainless Steel Cast 150# Fittings
Shop Stainless Steel Nipples
Shop Stainless Steel Forged 3000# Fittings
Shop Stainless Steel Flanges
Shop Stainless Steel Weld Fittings
Shop Stainless Steel Tubing
Perilla Seed Benefits For Skin,Perilla Seed Medicine,Perilla Seeds For Birds Food,White Perilla Seed For Birds
Jilin Chunyi Industrial Co., Ltd , https://www.perillaseed.com